
All About Hair Loss
Although it’s an important part of you, the hair on your head is probably something you take for granted.
-
You brush it, cut it, wash it, and you may spend hours a week styling it, but you might not think about how your hair grows or about it falling out until you notice more of your scalp in the mirror.
Whether you’ve just discovered clumps of hair in the shower or you’ve noticed a definite thinning and receding in key spots on your head, this guide can help you find out exactly what hair loss is, the signs of hair loss, and how to address and prevent hair loss.This menu will help you navigate this guide, and if you’d like, you can jump around from section to section.
Introduction
What Is Hair Loss?

That process is commonly known as alopecia.
Alopecia is a general term that refers to hair loss, but there are specific types of alopecia you may have. Take alopecia areata for example: it’s an autoimmune condition where your immune system will mistakenly attack your hair follicles.
Alopecia areata can strike anyone, and it may be due to genetics. Several members of the same family can have the condition, and it can appear as early as childhood for both men and women. It’s characterized by patchy, sudden hair loss on your scalp, face, and possibly other areas of your body.
Besides this round, patchy hair loss, there are a few other ways someone can suffer from alopecia areata:
-
Alopecia Totalis
Just like the name ‘totalis’ suggests, when you have alopecia totalis, you may lose every single strand of your scalp hair.
-
Alopecia Universalis
Alopecia Universalis is when you lose all of your body hair, from eyebrows to leg hair.
-
Ophiasis
When you can see a wave pattern around the back of your head around the edge of your scalp, that’s a form of alopecia areata known as Ophiasis.
-
Scalp health and hair loss
You may not realize it, but your scalp health is critical to facilitating hair growth. Your hair follicle will produce an oil called sebum, and if your follicle is full of sebum or somehow blocked by dead skin, infection, or dandruff, your hair growth could be impacted. If your hair follicle is completely blocked, hair growth may stop completely.
There’s also a condition called scalp folliculitis. This condition occurs when someone has/had a bacterial infection and the hair follicles become inflamed. That inflammation can present itself like a ring around the follicle, and you might think it looks a bit like acne.
If this condition is caught early, hair may still be present in the hair follicle. If the condition progresses, that hair may fall out. Scalp folliculitis can cause permanent damage to your follicles, and the damage can result in permanent hair loss.
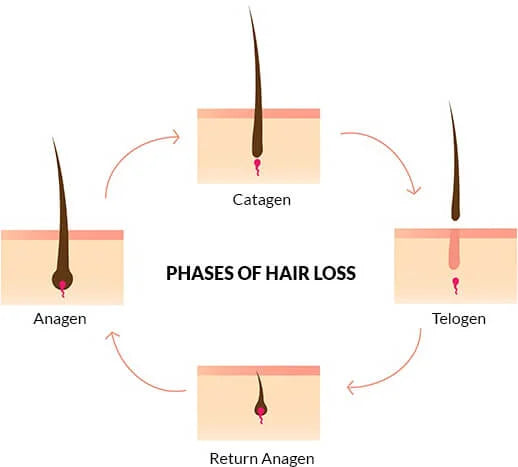
Hair Loss Cycle
The best way to understand the hair loss cycle is to look at how hair grows.
In a normal hair growth cycle, 90% of your hair is resting while about 10% is growing or shedding. Each follicle has a life cycle that can be divided into three phases.
-
Anagen hair growth
In this stage the hair root cells will divide as they are added to the hair shaft. This phase can last from 2 to about 6 years, and during that time it will grow about ¼ of an inch each month.
-
-
Catagen transitional phase
In the catagen phase your hair is no longer growing. During this transitional 2 to 3 week period, a club hair is formed. The club hair is formed when the hair follicle attaches to the hair shaft, and that attachment cuts off the follicle from both its blood supply and the cells that work to produce new hair.
-
Telogen shedding phase
This final phase of hair growth is also the phase where the hair loss cycle begins. The telogen phase lasts around two to four months, and as your hair begins to shed, the anagen phase will begin to produce new hair.
When you brush, shower, or style your hair, you will lose about 100 telogen-stage hairs a day. This is considered normal hair loss. Alopecia begins when you lose larger amounts of hair and the anagen phase begins to slow or is disrupted. One of the signs of hair loss is when the anagen phase begins to produce short, weak hairs. That can continue, or your body will cease to produce hair at all.
Psychological Effects
Facts About Hair Loss: Myths vs Facts
There are a lot of myths about hair loss.
There are a lot of myths about hair loss. From the concept of a single hair loss gene to whether or not too much styling can result in you losing your hair, it’s good for anyone going through hair loss to separate the myths from the facts. Here’s a few hair loss FAQs to help you understand fact from fiction.
-
Myth
You can inherit a hair loss gene from your parents or grandparents.
-
-
Fact
There is no single, identified gene that will result in you losing your hair. It’s the combination of both of your parents genes that can result in alopecia, baldness, or small spot hair loss.
-
Myth
Men suffer from hair loss more often than women.
-
-
Fact
It may not be as obvious in women because they may hide it well, but women do suffer from hair loss just as often as men do.
-
Myth
Your diet doesn’t affect hair loss
-
-
Fact
If your diet is lacking in vitamins and minerals for a long time, that may result in hair loss. Crash diets can also result in temporary hair loss.
-
Myth
If you use too many hair products or you tease, style, perm, or blow dry your hair excessively, that can cause hair loss.
-
-
Fact
Normal styling and blow drying will not result in hair loss. Because the follicles are under the skin, they are protected from any products or hot air. What styling and coloring can do is damage your hair or cause it to break
-
Myth
Trimming your hair or cutting it all off will make it grow more quickly and result in thicker hair.
-
-
Fact
Your hair growth depends on your own hair growth cycle, and that cycle is determined by genetic and environmental factors
-
Myth
Wearing a baseball hat or other tight hat on your head will lead to hair loss.
-
-
Fact
Your hair is not an organism that needs to breath, and as detailed in the hair growth cycle, only the root of the hair is alive. Wearing a tight hat won’t result in the suffocation of your hair, and you will not lose hair because of it.
Types of Hair Loss
There are many types of hair loss, and when someone begins to lose their hair, it can happen in various stages. Hair loss can be as mild as temporarily losing a small amount from a tiny area to becoming permanently bald.
There are also many other types of hair loss:
-
Androgenic Alopecia
Also called male pattern baldness or female pattern baldness, androgenic alopecia is a genetic condition that results in a receding hairline or lack of hair on the crown of the head.
-
Involution Alopecia
This is a natural condition that affects a large number of people. As you age your hair follicles go into a resting phase. The hair that’s left on your head becomes shorter and decreases in number, and the result is a natural thinning as you get older.
-
Anagen Effluvium
When you’re exposed to toxins like those found in chemotherapy, you may experience the sudden loss of hairs in the anagen phases. Known as anagen effluvium, the condition is reversible and your hair may regrow in as little as one to three months. Some people can experience permanent hair loss due to anagen effluvium.
-
Hair Loss Due to Stress
Stress and hair loss can go hand in hand. Stress can actually trigger a condition called telogen effluvium, where a large part of your hair may enter the resting phase all at once. When that happens, your hair can fall out or thin.
Stress induced hair loss resulting in telogen effluvium can be caused by both emotional and physical issues. A change in job, abrupt change in weight, the death of a family member are all common causes of this type of hair loss.
The good news is that stress induced hair loss is usually only temporary. It may take a few months, but once the stress or anxiety passes and you adjust, your hair should begin to grow back.
-
Dying Hair and Hair Loss
Will dying hair cause hair loss? Anyone who frequents a hair salon may wonder whether or not bleach or processing your hair with chemicals to color it will cause hair loss. The answer is, it depends.
The actual dying process will not stop your hair from growing, but it could cause hair loss because it damages the hair. Hair dye contains chemicals like hydrogen and ammonia, and applying those chemicals to your hair could cause you to lose excessive hair in the telogen phase. Hair dye is also strong enough to weaken the shaft of your hair, and that may cause breakage leading to hair loss.
If dying hair could cause hair loss, does hair gel cause hair loss? On its own, gel does not contribute to hair loss. What can become a factor is if you don’t focus on scalp health. If hair builds up, leaving you with a shiny scalp, you could eventually develop scalp folliculitis.
-
Hormonal Hair Loss
Hormone imbalance hair loss can happen to everyone, but it’s more likely to happen to women. Caused by fluctuations in hormones, hair loss hormone imbalance is common during pregnancy and menopause.
If you’ve ever wondered about birth control pills and hair loss, you won’t be surprised to find out that one may lead to the other. Because birth control pills may influence the growth and condition of your hair, so you can experience hair loss due to oral contraceptives. This generally only occurs if you already have a genetic predisposition to hormonal hair loss. It can also happen if you are especially sensitive to male hormones known as androgens.
Hormonal hair loss may be temporary as well, although it may take a few months beyond childbirth, menopause, or quitting birth control to begin growing back.
-
Hereditary Hair Loss
When someone begins losing a large portion or all of their hair, they usually take a look at their family’s hair first. Hereditary hair loss is called hereditary-pattern baldness or androgenetic alopecia, and this natural condition is due to genetics, hormones, and the aging process.
Hereditary hair loss often begins in the 20’s or 30’s, and while male-pattern baldness is more common, women may experience this type of loss--either before, during or after menopause.
-
How Your Diet Contributes to Hair Loss
When you go on a diet you restrict your body from accessing different types of foods. If you do that, you may also restrict your body from minerals and vitamins it needs to facilitate hair growth. That’s why eating disorders, poor diet, and extreme weight loss may result in temporary or permanent hair loss.
Having Hair and Having the Hair You Want Shouldn’t Be an Either/Or Proposition
You just need the right science, proven ingredients, and a dedicated team by your side.
When you notice thinning hair or hair loss, suddenly what you see in the mirror doesn’t match what you feel inside - and that can affect your confidence, your pride, and how you show up in the world.
But finding a real solution to thinning hair can feel like a roller-coaster of hope and despair.
It’s either cosmetic products that make big promises, but don’t help your thinning or receding hair. Or clinically proven products that stimulate growth, but leave you feeling like you’re trapped in a never ending bad hair day - wash, rinse, repeat.
We understand how frustrating the quest for great hair can be. So we made it our mission to eliminate the embarrassment of thinning hair.
The 3 Stages of Hair Loss For Women
Female hair loss can be devastating, and according to the American Academy of Dermatology, it affects about 30 million American women. Although there are several scales to help determine the stages in women’s hair loss for instance, theLudwig Scaleis the most commonly used method for creating a uniform analysis of hair loss in women. TheLudwig Classificationidentifies 3 unique stages of female baldness (androgenetic alopecia). Your doctor or dermatologist will use this classification system to better identify the three major factors in the diagnosis and treatment of female hair loss. These stages range from having thinning on the top of the head, to the scalp showing and, finally, loosing all of the hair at the crown of the head.
-
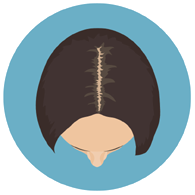
Stage One
It’s normal to lose between 50 to 100 hairs per day, and when the frontal hairline remains relatively unaffected, most women won't even notice that a mild hair loss has occurred. If hair loss occurs on the top and front of the scalp, it will be more likely noticeable with middle part hairstyles.
-
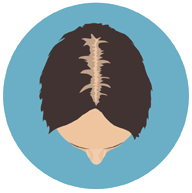
Stage Two
In stage 2, women usually notice some thinning, shedding, and a general reduction in hair volume. Your middle part will keep on widening over time.
-

Stage Three
Stage three is the final and most extremestage of female hair loss. Hair density is so thin on the crown (top of the head), that it makes it hard to hide and becomes visible to the naked eye.
Treatment for Women Hair Loss
-
Treatment for Stage 1
During these stages you may not be seeking intensive hair loss treatment, but you should be getting in front of the issue all the same. Taking preventive measures with an anti-aging, pro-growth, anti-thinning shampoo and conditioner is recommended. Leave-in topical sprays are also a good offensive measure to encourage robust growth in trouble areas. In the early stages, when it's easiest to forestall future losses and counteract recent issues, optimizing your hair and, more importantly, scalp health is essential.
-
Treatment for Stage 2
Your hair will have begun to noticeably and progressively thin, but you still have drug-free hair loss treatment options during these middle stages. The best defense is pairing a hair loss shampoo, conditioner and topical treatment with hair-specific vitamin supplements (such as Biotin). A complete evaluation of potentially aggravating lifestyle factors should also be undertaken: diet, stress levels, exercise regimens, sleep patterns, u/v exposure--they all exacerbate poor hair and scalp health.
-
Treatment for Stage 3
When a women has later stage hair loss, they want to spend time researching both drug-free, drug-based and surgical-based hair loss treatments. There are treatment options that can be tailored to your specific type or stage of hair loss, and you will want to explore all options that offer you the best chance of regrowth. Typically this late in the hair loss spectrum, multiple measures will need to be taken to revert losses and avoid continuing deterioration.
Stages of Hair Loss For Men
Androgenic alopecia is the most common cause of thinning hair, and it’s estimated half of the male population aged 40 and over will suffer from this problem. In some cases, hair loss will start as a gradual thinning, progressing in different parts of the head to complete baldness as the person grows older. In other cases, hair loss starts at ages younger than 40, and unless alopecia is treated at the beginning stages of hair loss, it can quickly become worse.
Androgenic alopecia involves the miniaturization of hair follicles. These follicles will become smaller and smaller, producing short, thin, and brittle hair. In some cases, hair follicles may eventually stop producing any hair. Not only do the hair follicles get smaller, they may actually disappear completely.
The 7 Stages of Hair Loss For Men
According to the Hamilton-Norwood Classification, originally published in 1975, there are 7 stages of male pattern baldness. Your doctor or dermatologist will use this classification system to identify two main and many minor forms of alopecia. These stages range from having a full head of hair to thinning and, eventually, complete baldness.
-

Stage One
It’s normal to lose between 50 to 100 hairs per day, so for the average person, stage one hair loss might not look like anything is out of the ordinary. The hair line and growth appear normal, and even a slight recession isn’t noticeable. At stage one you may have a full head of hair, but you may have also noticed you’ve lost a few more strands beyond what you’d consider normal.
-

Stage Two
In stage two hair loss you’ll begin to notice thinning. The focus could be a receding hairline on your forehead, the crown of your head, at your temples, or right in the center of your head. A symmetrical triangular shape could appear as hair recedes.
-

Stage Three
Stage three is the earliest point in the scale where baldness is identified. Your hairline at your forehead and temples will be receding rapidly, high temples become common, and you may see a significant thinning on the crown of your head.
-

Stage Four
When you are at stage four hair loss, some parts of your hair will continue to thin while others will be void of hair. You may find the naked areas are still covered in fuzz, or you may have a few lone hairs in different spots. This is the stage where round balding appears on top of the head.
-

Stage Five
You’ll notice a narrowing and thinning of the hair that’s still growing between the crown of your head and your receding hairline. You may even notice a small island of hair that sits high on your forehead, leaving you with one small spot of hair and several naked areas around it.
-

Stage Six
Any bridge or island between your forehead and your crown has now receded, and hair will continue to fall out to create a wider section with no hair at all.
-

Stage Seven
When you’re at stage seven, the hair on the top of your head is almost completely gone. Your head could have a large area without hair surrounded by a ring of hair that encircles your head. Any remaining hair will continue to fall out.
Treatment for Men Hair Loss
-
Treatment for Stage 1-3
During these stages you may not be seeking intensive hair loss treatment, but you should be getting in front of the issue all the same. Taking preventive measures with an anti-aging, pro-growth, anti-thinning shampoo and conditioner is recommended. Leave-in topical sprays are also a good offensive measure to encourage robust growth in trouble areas. In the early stages, when it's easiest to forestall future losses and counteract recent issues, optimizing your hair and, more importantly, scalp health is essential.
-
Treatment for Stage 4-5
Your hair will have begun to recede rapidly, but you still have drug-free hair loss treatment options The best defense is pairing a hair loss shampoo, conditioner and topical treatment with hair-specific vitamin supplements (such as Biotin). A complete evaluation of potentially aggravating lifestyle factors should also be undertaken: diet, stress levels, exercise regimens, sleep patterns, u/v exposure--they all exacerbate poor hair and scalp health.
-
Treatment for Stage 6-7
When someone has stage six or stage seven hair loss, they want to spend time researching both drug-free, drug-based and surgical-based hair loss treatments. There are treatment options that can be tailored to your specific type or stage of hair loss, and you will want to explore a few that offer you the best chance of regrowth. Typically this late in the hair loss spectrum, multiple measures will need to be taken to revert losses and avoid complete baldness.
How to Prevent Hair Loss
Anyone who has felt helpless while watching their hair fall out will wonder how to prevent more hair loss. The answer is that future deterioration in hair conditions (quality and quantity) is about playing offense and defense. It’s about your hair and scalp health.
The earlier you start caring for your hair and scalp, the better off you’ll be. A large part of the population will suffer from hair loss, and they don’t begin seeking a hair loss solution until they’ve already lost 30% of their hair.
Taking care of your hair right now includes:
- Regularly washing your hair with an anti-aging, growth stimulating shampoo and conditioner
- Changing your diet to include protein and vitamins
- Minimize stress and nurture a healthy overall lifestyle!
- Avoiding gels, pomades, sprays or any other product that are alcohol-based
- Avoid any hair product with cheap, harsh ingredients: sulfates, parabens, phthalates, silicones, etc.
All About Hair Loss
Women & Hair Loss
Although it’s perceived as more common that men will lose their hair, women experience hair loss/thinning as well. The causes of female hair loss vary including pregnancy, hormones, menopause, or female pattern hair loss. Female hair loss can have a devastating effect on self-esteem, mental well-being, and even physical health.
Men & Hair Loss
Men experience three main types of hair loss: androgenic alopecia, telogen effluvium, and alopecia areta.
Hair Loss FAQs
When someone begins to experience hair loss or thinning, they have a lot of questions. A lot of those questions were answered in different sections of this page, but there are some additional hair loss FAQs you may be interested in.











